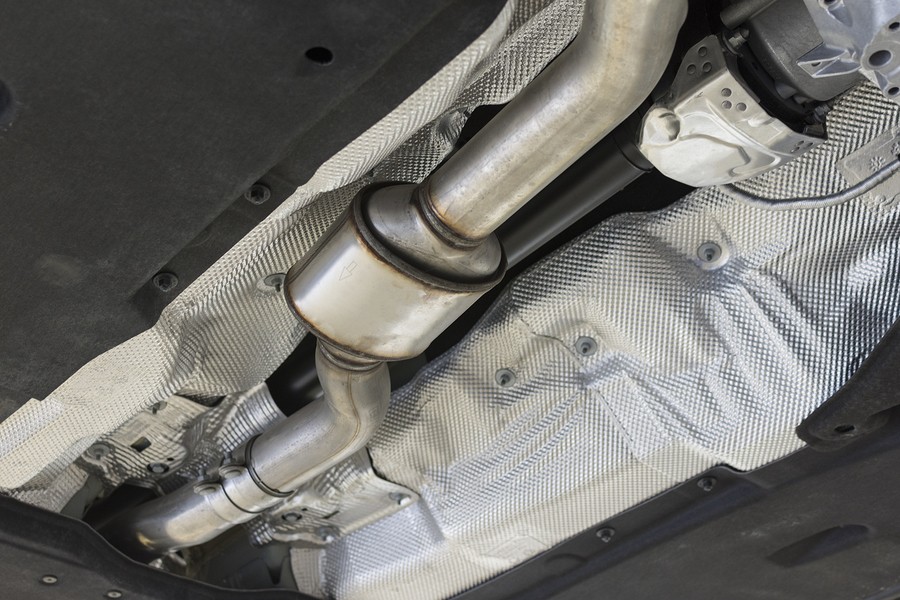
The catalytic converter is designed to reduce harmful emissions from gasoline-powered engines by converting carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and NOx into water vapor and non-harmful gases.
Your catalytic converter must be working properly, or you may risk violating smog and EPA emission standards, as well as the Federal Clean Air Act. However, there are some instances where your catalytic converter fails.
If you're wondering how to tell if your catalytic converter is failing, then you're in the right place. This article will outline ten important symptoms to look out for. Keep reading to learn more!
What is a catalytic converter, how does it work, and what does it do?
A catalytic converter is designed to reduce harmful pollutants (NOx, hydrocarbons, and carbon monoxide) that are released into the air by your vehicle's engine. By converting these unburned gases back into water vapor and non-harmful emissions, catalytic converters help protect your car's engine while protecting the environment.
The importance of the catalytic converter
All modern vehicles manufactured since the late 1970s have been equipped with a catalytic converter, including both gasoline and diesel engines. As a result, approximately 17 million cars on the road today contain at least one onboard catalyst.
The importance of the catalytic converter is to make our air cleaner as it reduces harmful emissions from vehicles, thus limiting carbon dioxide buildup in the atmosphere. The catalyst converts toxic NOx into nitrogen, water vapor, and carbon dioxide, which is not harmful to humans or animals.
Since your vehicle's catalytic converter needs high temperatures (at least 2000 degrees Fahrenheit) to function properly, an under-performing one can result in poor fuel economy, lack of power, reduced engine performance and increased emissions due to incomplete combustion.

How to Tell if Your Catalytic Converter is Failing? 10 Important Symptoms!
Now that you know what a catalytic converter does and its importance, here are ten symptoms of an underperforming catalyst. If any of the following signs sound familiar, then your catalytic converter may be on its way out:
1. Your Check Engine Light is on:
When your check engine light comes on, one sure sign of an issue with your catalytic converter. The check engine light – also known as “Service Engine Soon” or “Check Engine” – illuminates any one of several issues that your car's computer has detected.
Given that the catalytic converter is a major part of your vehicle's emissions system, it may be one of the causes for this indicator to appear on your dashboard. Without proper exhaust gas recirculation and catalytic reduction, you run the risk of putting excess pollutants into the air you breathe.
2. You've recently had a smog or emissions inspection:
One of the most important things to remember is that the catalytic converter has nothing to do with fuel economy, engine power, or general performance. As such, it's unlikely that your catalytic converter will suddenly break down after you've just had an emissions test performed on your vehicle.
However, this symptom can still be wary since some states require periodic inspections and maintenance for older vehicles.
3. The check engine light comes on when you accelerate:
If you notice your check engine light coming on whenever you step down on the gas pedal—but turn off once you return to cruising speed—then the chances are good that there's a problem with your car's catalytic converter.
This symptom may not be due to the catalytic converter itself but could also indicate an issue with your car's oxygen or O2 sensors. This separate system monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
4. The check engine light stays on after you've just had it serviced:
If you've just had the spark plugs changed in your vehicle and then later notice that the check engine light is still illuminated, this could be a sign of trouble. In some cases, mechanics have been known to accidentally disconnect a wire from either one or more cylinders' positive or negative side.
This results in a lack of power and reduced acceleration while driving—which can cause unexpected illumination of the check engine light. To keep this from happening, be sure to have a professional check your vehicle's catalytic converter before having the ignition components replaced.
5. There's a rattling noise coming from under the hood:
A weak or failing catalytic converter can result in various symptoms that will vary depending on the cause and each car.
Common signs include a “rattling” noise coming from under your hood—which could sound like muffler bearings or belt – as well as higher than normal exhaust temperatures (due to poor heat dissipation) and reduced fuel economy. If you hear any of these sounds, it may be time for a replacement.

6. Your gas mileage has gone down
Red engine power and increased emissions levels are the two main symptoms of a clogged or damaged catalytic converter. Both of these, in turn, reduce your vehicle's gas mileage—which can often be one of the first signs that there is an issue.
Go for a few quick runs to test what's going on with your car and see if this symptom is due to a faulty catalytic converter. If you notice that you're not getting as many miles per gallon as usual, then you should get your emissions tested and take it in for replacement.
7. You've replaced your spark plugs:
One common reason why an oxygen sensor or O2 sensor will cause the check engine light to come on is replacing the spark plugs in your vehicle. It's possible for mechanics to accidentally disconnect either the positive or negative wire from one or more cylinders when working on your vehicle's ignition components—which results in a lack of power and reduced acceleration while driving.
It'll likely cause increased emissions levels and an illuminated check engine light if this happens. To keep this from happening, be sure to have a professional check your vehicle's catalytic converter before having the ignition components replaced.
8. There are visible signs that something is wrong with the exhaust system:
A clogged catalytic converter, among many other emission-related issues, can result in higher than normal exhaust temperatures (due to poor heat dissipation) and reduced fuel economy.
The best way to avoid both of these issues is by having your vehicle's catalytic converter replaced. Also, keep in mind that certain types of damage to the exhaust system can result in elevated emissions levels—which, again, may cause the check engine light to come on.
9. You've had several repairs done recently:
If you've just had several repairs done on your car—such as the ignition components being replaced or other maintenance issues corrected—and have noticed no change in performance following the work being done, then it may be time for a new catalytic converter.
The problem could also be due to either an issue with your oxygen sensor or O2 sensors, part of a separate system that monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust fumes. Either way, if you notice problems, visit your local automotive service center for a free replacement.
10. Your catalytic converter is old:
A clogged catalytic converter, among many other emission-related issues, can result in higher than normal exhaust temperatures (due to poor heat dissipation) and reduced fuel economy.
If you notice either of these symptoms and they're happening more frequently, then it may be time for a new catalytic converter. Keep in mind that the average lifespan of a particular component will vary from car to car—so some may have shorter or longer life expectancy depending on how well they were made and maintained throughout their life cycle.

How to replace a catalytic converter?
if you decide to replace your catalytic converter, you need to follow these simple steps:
#1 confirm you're able to replace the converter and understand the risks and
Before moving any step further, if you're not familiar with the process, we strongly recommend hiring a professional, experienced mechanic who knows how to disconnect and remove your catalytic converter safely.
#2 choose your working area
Find a place for your vehicle with good ventilation, ample space, and easy access to the underhood.
#3 disconnect battery
Disconnect your car's battery before moving forward. Negative or any exposed metal parts might cause a short circuit.
#4 make sure there are no fuel leaks
Fuel system lines can be easily damaged if carelessly handled. Use some paper towels or shop rags as a precaution.
#5 jack up car and remove wheels
Use a floor jack to raise the car for additional working space. Box end wrenches will help you to move forward but be sure they're correctly positioned not to damage exhaust system components. Finally, remove both front tires and set them aside in a safe place away from your work area.
#6 remove the heat shield
Remove the metal heat shield from the catalytic converter assembly with a 10 mm wrench or ratchet. It's attached by two bolts on each side of the vehicle so that it won't take much time, but be extremely careful not to damage surrounding parts such as oxygen sensors, brake lines, or gas tanks. Also, avoid scratching up the paint with sharp metal edges.
#7 disconnect muffler hangers
Using your ratchet or wrench, loosen bolts on both sides of your vehicle's catalytic converter system. These are attached to rubber hangers which you need to remove as well. Using pliers for this process can result in breaking them, so it's advised to use a set made for this specific task, but if they're too damaged—you might want to consider replacing them with new ones.
#8 separate catalytic converter from the exhaust pipe
Use a large adjustable wrench or crescent wrench to rotate the assembly counterclockwise. Be careful not to damage aluminum oxide silencer donuts by using a tool that's too large and causing damage. Use a ratchet and extension if you can't rotate the converter because of tight space.
#9 remove clamps
Remove all three nuts holding catalytic converter to exhaust pipe. You should be able to disconnect it by hand at this point. However, suppose it's being held with any other type of fastener. In that case, you may have to use a wire cutter or reciprocating saw to cut off its head so you can loosen the assembly enough for removal purposes.
If your engine emits an unusual noise while running—you need to stop working immediately! The heat from the welding process will cause it to overheat, leading to severe damage—repair that issue before continuing.
#10 Install a new catalytic converter
Attach a new catalytic converter using the same fasteners you removed earlier. Never tighten them completely at this point—you need to attach your muffler hangers back first and then follow the torque settings from the factory service manual.
The final step is installing heat shields, wheels, and front tires if you haven't done that already. Next, lower the vehicle back on the ground using a floor jack. Finally, reconnect the negative battery terminal, remove wheel chocks and take your car for a test drive afterward.
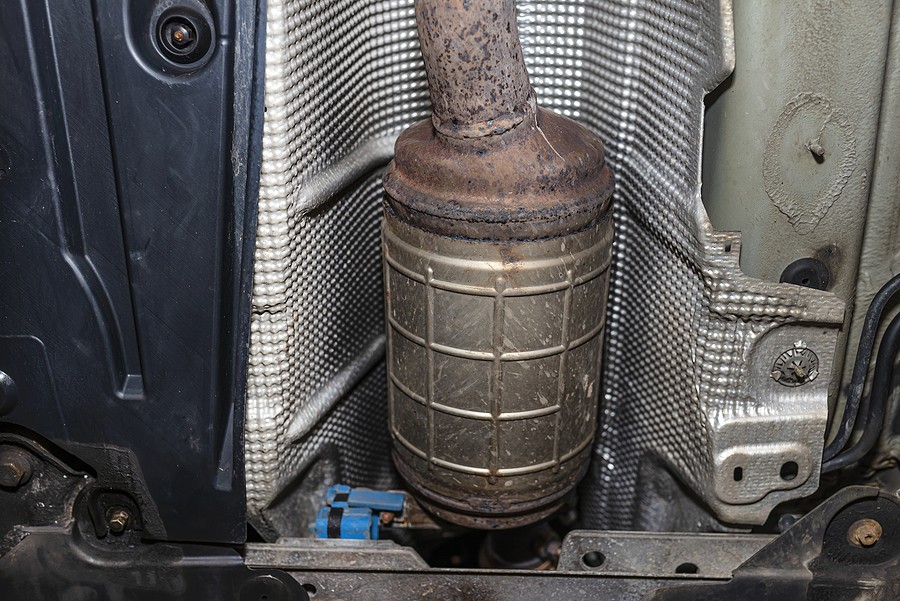

Tips for maintaining your catalytic converter :
To protect your catalytic converter from damage, it's highly recommended to install one of these DIY tips. Any professional mechanic will tell you this is one of the most important maintenance processes you can do to extend your vehicle's performance and durability.
More specifically, here are 5 top tips to consider to prevent early catalytic converter damages:
- Follow your factory service manual for exact torque settings; otherwise, you might damage it or excessively stress exhaust system components.
- Use the same type of fastener to attach heat shields and muffler hangers. Replacing one type with another may cause leaks and decrease the converter's performance over time.
- Never cut off anything attached to catalytic converter assembly, even if there's no other way around—that could be potentially hazardous for anyone working on your vehicle. Instead, always try to remove old hangers using pliers first—it can save you both time and money. If that doesn't work, use a wire cutter instead of a reciprocating saw, or any other tool may generate sparks that are harmful to you and your car's engine.
- If you have to raise the vehicle—use a set of jack stands or a full-sized hydraulic floor jack. Never try to use bumper jacks or other types for this specific task because they're not safe enough.
- Remove rust from the catalytic converter using a grinder, wire brush, or sandpaper before installing. Factory fasteners may be corroded, too—use a wire brush to clean them off so you can apply a fresh coat of anti-corrosive.

Conclusion
This article highlighted ten important symptoms to answer the question “How to Tell if Your Catalytic Converter is Failing?” These symptoms range from simple issues like a bad or faulty O2 sensor to severe issues like a complete meltdown in your catalytic converter. So read on and replace your catalytic converter immediately!
If you experience any of these ten symptoms, your catalytic converter may be on its last leg. If this is the case and you want to prolong the life of your car or truck, it's time to replace that old part with a new one. Please make sure you pay attention to every symptom we mentioned so that you can find out what needs replacing first!



