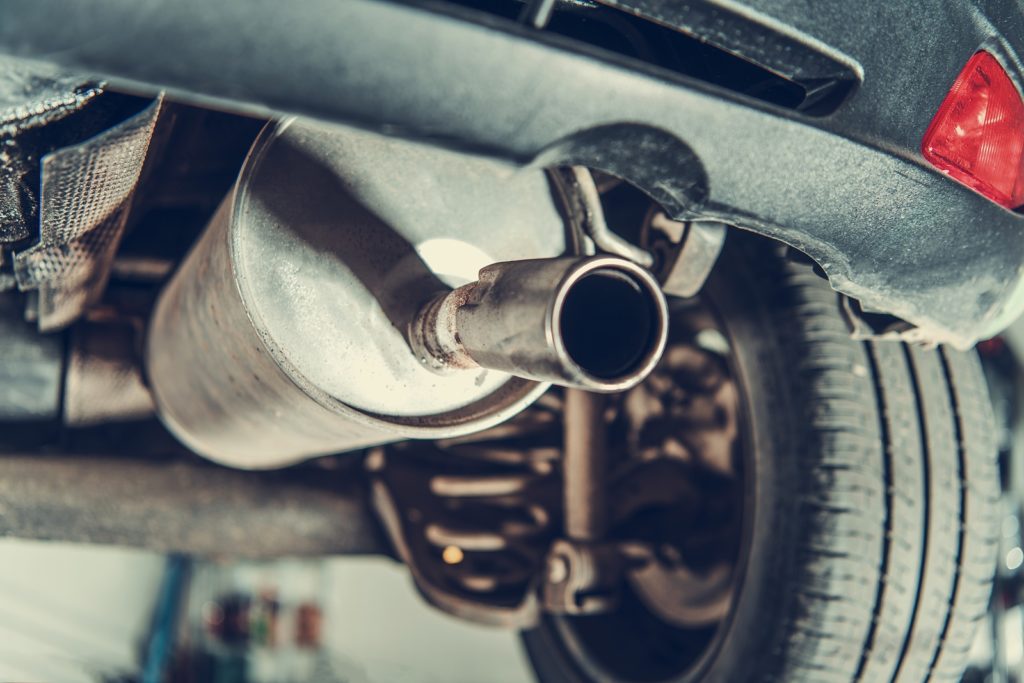
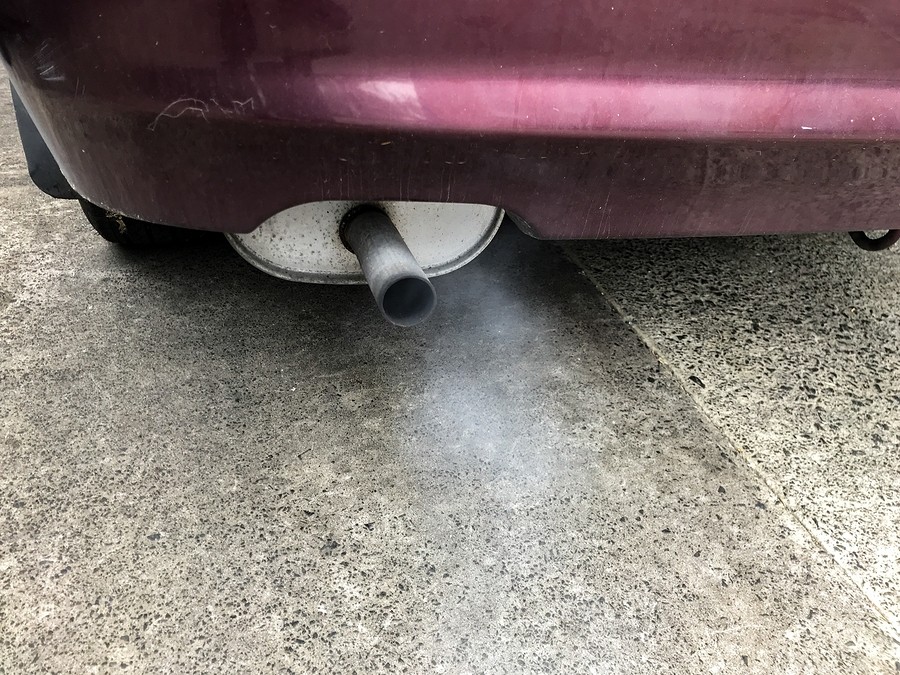
In the United States, 31 of the 50 states require an emissions test (commonly referred to as a smog test) in order to register the vehicle within their respective states. These tests are generally performed on an annual or biannual basis and often accompany a full vehicle inspection as well as a comprehensive emissions test.
Vehicles that are not mechanically sound are often malfunctioning to the point where their emissions are higher than predefined limits. These limits vary per state. Vehicles have a complicated emission control system that is designed to keep polluting elements out of the air. There isn't one component, but several pieces working together to ensure that a vehicle is not putting out harmful emissions.
If you fail a smog test, you will not be able to register your vehicle. This can lead to fines, penalties and other legal issues that go along with an out of date or expired registration. On top of the financial element, if your vehicle fails a smog test then there is no doubt it is putting out way more pollutants than it should be. Since tailpipe emissions are a leading cause of pollution, the EPA and several leading state agencies have recommended a strong course of action to alleviate gross polluters.
This article will cover the components of an emissions control system, how tests are performed and the top reasons why vehicles fail emissions tests. We will also cover what the average repair cost is for each of these common issues. Some are easy DIY type fixes, and some are much more complicated and will require the work of a professional mechanic. Read on to learn more.

What Exactly Does An Emissions Test Check For?
A smog check measures pollutants that are coming out of your vehicle's tailpipe, including the volume of these pollutants at different engine speeds. In addition to measuring pollutants, an emissions test is also going to look at your vehicles on board diagnostics system or OBD, which can indicate issues such as misfiring cylinders or an overly rich air/fuel mixture. Most emissions tests also include a visual inspection to look for things like leaking oil or other fluids that may contaminate the environment.
Emissions tests measure levels of nitrogen oxide (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), particulate matter (PM), non-methane organic gases (NMOG), and formaldehyde (HCHO).
Components Of An Emission Control System
There are several components to a functional emissions system. These components are constantly in use and as a result can wear out over time and cause your car to fail an emissions test. Let’s cover a few of these common components and their operation.
PCV Valve: A PCV or positive crankcase ventilation valve is designed to take vapors produced in the crankcase during combustion and recycle them back into the vehicles air/fuel mixture. These vapors need to be carefully mixed in, as they can dilute the air/fuel mixture to the point where performance is affected. A malfunctioning or clogged valve can allow pressure build in the crankcase which can allow oil leaks to form. This loss of vacuum (engines are a sealed system) can make an engine sputter or backfire.
EGR Valve: The EGR or exhaust gas recirculation valve is designed to allow a small amount of exhaust gas back into the air/fuel mixture for a vehicle. This is another measure to minimize pollutants by reintroducing them into the engine for further processing. It’s most effective at monitoring and controlling oxides of nitrogen that are naturally produced during the combustion process. This is a very serious pollutant. Your car's computer carefully reintroduces exhaust gases in trace amounts back into your engine and any malfunction will have an immediate effect on performance.
Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is essentially a secondary combustion chamber for unspent pollutants coming from your engine. It’s constructed of highly heat resistant materials and contains a special catalyst plate to speed up the oxidation process of pollutants. Essentially, pollutants pass over a palladium or platinum plate and are quickly oxidized and converted into carbon dioxide and water vapor. Excessive heat is produced in this process and over time a dirty engine will ruin a catalytic converter.
O2 Sensor: The sensors are typically located before and after the catalytic converter. While older cars have two, many newer cars have up to four of these sensors. Their primary job is to monitor and control the air fuel ratio which is essential to the effective operation of a vehicle. They are extremely sensitive and tightly calibrated to OE standards. These can often be a simple replacement but ignoring them can lead to other critical components failing.

Emissions Test Process
Emissions test processes vary per state but only slightly so. Depending on the age of your vehicle, one of two tests will generally be performed.
1. OBD test. OBD or Onboard Diagnostics references your cars computer to verify proper functionality of all systems. Cars built after 1995 have an OBD port that is specially designed to allow OBD diagnostic tools and emissions test systems to connect to it.
2. Cars built between 1981 and 1995 may be subjected to a I/M240 Dynamometer test. This basically hooks your car up to a machine that simulates various road speeds and measures your cars emissions at the tailpipe.
The following steps are performed regardless of the age of a vehicle:
1. The technician will visually inspect the cars undercarriage and engine bay for obvious signs of leakage.
2. Checks will be performed on the gas cap to ensure proper sealing
3. A visual check for smoke and a visual check for the vehicles ‘check engine’ light
4. Functional check of vehicles ignition timing, exhaust gas recirculation system and fuel evaporative system.
5. The technician will also inspect for the presence of a catalytic converter and obvious vacuum leaks or holes in the system.
Once complete, the technician will present you with a pass or fail certificate, including a full presentation of all data collected during the test. This information is then uploaded to a central database and is tied to your vehicles VIN.
If you have failed, it’s time to start figuring out why!
Will I Fail If I Have A Check Engine Light?

The check engine light is something that is so commonly ignored by average consumers that it almost becomes a joke at times! The reality is that a check engine light is not to be ignored especially when it comes time for an emissions test.
Simply having a check engine light active on your vehicle will immediately fail you for an emissions test. The reason is actually quite simple. The check engine light is there to monitor your cars essential components and if there is a malfunction in these components, it is highly likely your car is not operating at optimal levels.
As you’ll see below, many of the issues that can cause you to fail an emissions test tie back to a check engine light.
Pre-Diagnosis Check
Prior to rolling into an emissions test, if you have a check engine light showing, you can easily get the reason for that check engine light diagnosed. Cars built after 1995, as mentioned above, have an OBD port that allows an auto shop to hook up its diagnostic equipment. This equipment can tell you exactly why your car is showing a check engine light!
A little known fact is that most car part retailers, like Autozone, will diagnose your check engine light for free. It’s better to know what you’re dealing with prior to going into the emissions test, especially if it’s an easy fix.
This can save you a lot of hassle!
Let’s talk about some common reasons why a check engine light may be on and why you may be failing your emissions test.
Rich Air/Fuel Mixture
If too much fuel is being combusted during an engine cycle – your car will fail based on the overly rich air fuel mixture. This condition will lead to your car burning fuel inefficiently and the result of this excess of fuel is increased emissions at the tailpipe. Occasionally, so much fuel can be dumped into an emissions system that an entire catalytic converter can fail!
This can happen due to malfunctioning fuel injectors or a malfunctioning oxygen sensor.
A fuel injector’s purpose is to effectively deliver fuel to the cylinder of an engine. If an injector is delivering too much or too little fuel – then the motor will run inefficiently. If two little fuel is delivered, the motor will sputter and choke. If too much feels delivered then the motor will burn off the excess fuel and the net result is increased emissions.
The oxygen sensor is a device that is used to measure the oxygen levels in the air and fuel of the vehicles engine. It sends signals to the car’s computer which then indicates to the car’s computer if there is too much or too little oxygen in the mixture. Since oxygen is required for fuel to burn, it needs to be kept at an optimal level.
Cost To Repair O2 Sensor: $95 (DIY) to $470 (Pro)
Cost To Replace Injectors: $1121 to $1407 (Pro only, not a recommend DIY job)
Defective Spark Plugs
Spark plugs are another absolutely essential component of a motor that is often overlooked before an emissions test. These simple pieces are required to effectively burn the air fuel mixture being introduced into the engine cylinder. If they are not functioning properly, then the air fuel mixture is not being burned properly and can lead to increased emissions at the tailpipe.
Fortunately, an advanced, DIY savvy individual can replace all the spark plugs on the vehicle in an afternoon.
Cost to replace spark plugs: $100 (DIY) $350 (Pro)
Leaking EVAP System
Every vehicle has a system of tubes and seals to effectively keep gasoline vapors from entering the atmosphere and then recycling unused vapor back into the tank. This is commonly known as the evaporative vapor emissions control system or EVAP. The challenge of a malfunction in this type of system is it that it can be incredibly difficult to track down and fix!
This type of issue is often indicated by a check engine light.
Cost to replace EVAP canister: $450 to $560 (Pro recommended only)
This cost can be much higher if the leak is not obvious!
Loose Gas Cap
It may seem like a completely ridiculous reason to fail and emissions test but it happens all the time! Over time, a gas cap can become loose and let out vapors from the gas tank into the atmosphere. This loss of pressure will cause your vehicle's computer system to register a fault and most likely a check engine light.
In my experience this is one of the first things I tell people to do if they have a check engine light test or have failed an emissions test. Why? It’s cheap!
Cost to replace gas cap: $10-25 (DIY)
Bad Mass Air Flow Sensor
The mass flow sensor is used to determine the flow rate of air entering an internal combustion engine. The air mass information is necessary for the engine control unit to balance and deliver the correct fuel mass to the engine. If this simple sensor is malfunctioning, an engine will not work efficiently and will cause the check engine light to go off OR create additional emissions at the tail pipe of the vehicle.
Cost to replace a mass air flow sensor: $60 (DIY) $300 (Pro)
Catalytic Converter
When a catalytic converter malfunctions, it is no longer able to effectively utilize its catalyst system to convert pollutants into carbon dioxide and water. If your engine is running poorly, there’s a good chance that your catalytic converter has been working overtime. This will cause it to fail. As with most things with an a vehicle, issues with an engine are usually a domino effect. If you do not maintain your vehicle properly, subsystems that are ancillary to maintenance will begin to fail.
This is one of the most expensive repairs you can do on your vehicle! As mentioned above, there are precious metals within a catalytic converter that go for a very high amount of money on the market.
Costs also range greatly on catalytic converters due to the type of vehicle or brand of vehicle you own.
Cost for catalytic converter: $1000 to $3000+ (Pro)
Leaking Exhaust System
There are several reasons why an exhaust system may start to leak. Typically it is either a vehicle that is older or a vehicle that is exposed to road elements like salt. Despite old age, a vehicle's exhaust can also be damaged by an accident or road debris.
If an exhaust system is not sealed, it will not allow the gases from the engine to be burned by the catalytic converter. Sometimes an exhaust leak can also be visible and heard by a skilled technician. This will cause an immediate failure for an emissions test.
Cost to repair exhaust system: $150 to $2000 (pro) depending on the location and severity of leak.
Passing The Smog Test
There are essentially two large elements to passing a smog test on an annual or biannual basis. Maintenance and repair.
First off, proper maintenance of your vehicle is absolutely essential. If you properly maintain and replace parts at the pre-described intervals according to the manufacturer's guidelines, there is little chance these parts will fail when it comes time for an emissions test. Think about the example of spark plugs, or even fuel injectors. Either one of these things can easily be repaired or maintained throughout the course of the vehicles lifespan but can prove costly in the long run if not maintained.
Sometimes, despite all of our best efforts, a vehicle will not pass the smog check due to part failure or bad design. Being proactive about figuring out what is wrong with your car prior to taking it down for an emissions test will allow you to control cost and final results. At times, you are just going to have to buck up and pay to get your car fixed so it can pass the test.
Retaking The Smog Test
While most shops will allow you to retest for free, there is an absolute limit on how many times they will let that happen. I once owned an old Toyota 4Runner that needed a ton of work prior to passing a smog test. After initially failing a smog test, not once but twice, upon my third return back to the shop I was then informed that the policy was a strict two retests. Looking back on it now, I should have more thoroughly diagnosed the problem instead of trying to guess what the issue was based on the data from the smog test.
Although not passing a smog test can seem like a huge issue, properly diagnosing the issue and properly maintaining your vehicle will lead to the best possible result! Information is power!